Effective Use of C Sharp Collections Dev
Are you
aware that most developers do not use C# collections effectively?
The reason is that they don't
experience a performance difference unless they manage or manipulate large
datasets.
This document doesn't cover all
topics related to C# collections; it only addresses a few collections from both
generic and non-generic types.
Introduction
The diagram below shows the
namespaces and their supported collections. This document covers the items
highlighted in green in the diagram.
Collections allow for dynamic memory allocation for operations such as adding, updating, deleting, searching, and sorting items.
Generic Collection
- Type Safety: It is strongly typed, ensuring consistent data types within a collection. Otherwise, we get a compilation error.
- No boxing is needed
- There is no data loss due to type mismatch.
- Deliver better performance
Non-Generic Collection
- No Type Safety: A collection can store elements of any data type.
- Boxing might be necessary.
- There is no guarantee of data availability
- Data type mismatch can occur at runtime.
Add / Insert Data into a Temporary Collection
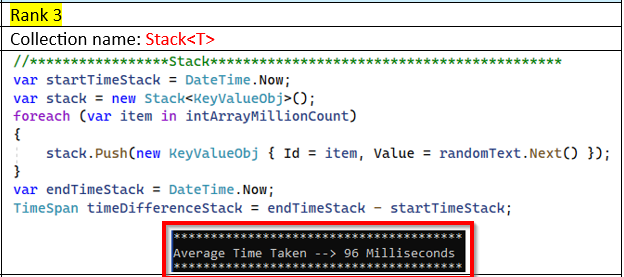
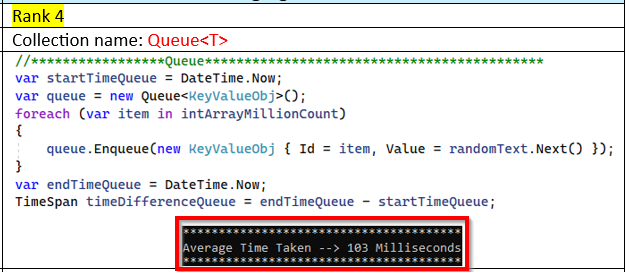
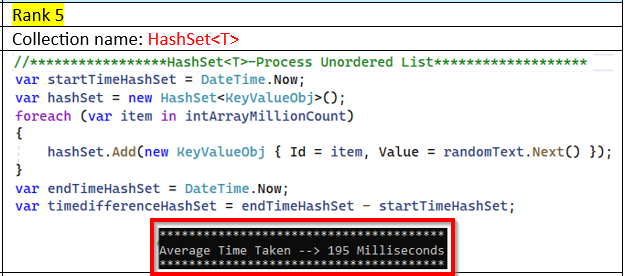
This section will demonstrate the performance in milliseconds when a million data elements are inserted into a collection object.
Test Scenarios
Input Data: Int[] intArrayMillionCount = int[1000000]; This integer array will contain both ordered and unordered lists of random numbers to be inserted into various C# collections.
Process: A million pieces of data will be processed five
times, and the average time will be recorded.
Note: The performance measurements may vary depending on the PC configuration.
Calculation Using a Large Temporary Collection
This section will demonstrate the performance in milliseconds when carrying out a task with a million data elements.
Test Scenarios
Input Data: Int[] intArrayMillionCount = int[1000000]; This integer array will contain both ordered and unordered lists of random numbers to be inserted into various C# collections.
Process: Calculate the sum of 1000 elements that are greater than 75,000 from a collection containing one million elements.
Note: The performance measurements may vary depending on the PC configuration.
OrderBy in queries. As demonstrated in the exercise above, ordered lists perform better than unordered lists.






















Comments
Post a Comment